Expansion bolts for concrete applications in buildings and elevators
DIN 6923 Hexagon Flange Nut
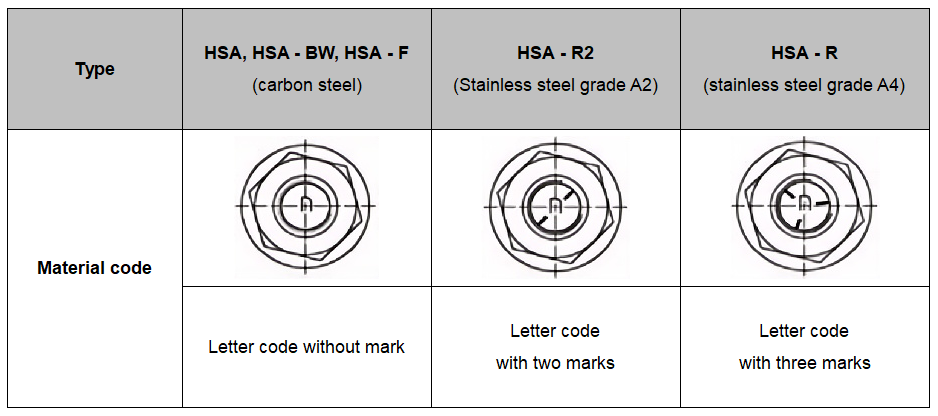
Letter code for anchor length and maximum thickness of the fixture tfix
|
Type |
HSA, HSA-BW, HSA-R2, HSA-R, HSA-F |
|||||
|
Size |
M6 |
M8 |
M10 |
M12 |
M16 |
M20 |
|
hnom [mm] |
37 / 47 / 67 |
39 / 49 / 79 |
50 / 60 / 90 |
64 / 79 / 114 |
77 / 92 / 132 |
90 / 115 / |
|
Letter tfix |
tfix,1/tfix,2/tfix,3 |
tfix,1/tfix,2/tfix,3 |
tfix,1/tfix,2/tfix,3 |
tfix,1/tfix,2/tfix,3 |
tfix,1/tfix,2/tfix,3 |
tfix,1/tfix,2/tfix,3 |
|
z |
5/-/- |
5/-/- |
5/-/- |
5/ -/- |
5/-/- |
5/-/- |
|
y |
10/-/- |
10/-/- |
10/-/- |
10/-/- |
10/-/- |
10/-/- |
|
x |
15/5/- |
15/5/- |
15/5/- |
15/-/- |
15/-/- |
15/-/- |
|
w |
20/10/- |
20/10/- |
20/10/- |
20/5/- |
20/5/- |
20/-/- |
|
v |
25/15/- |
25/15/- |
25/15 |
25/10/- |
25/10/- |
25/-/- |
|
u |
30/20/- |
30/20/- |
30/20/- |
30/15/- |
30/15/- |
30/5/- |
|
t |
35/25/5 |
35/25/- |
35/25/- |
35/20/- |
35/20/- |
35/10/- |
|
s |
40/30/10 |
40/30/- |
40/30/- |
40/25/- |
40/25/- |
40/15/- |
|
r |
45/35/15 |
45/35/5 |
45/35/5 |
45/30/- |
45/30/- |
45/20/5 |
|
q |
50/40/20 |
50/40/10 |
50/40/10 |
50/35/- |
50/35/- |
50/25/10 |
|
p |
55/45/25 |
55/45/15 |
55/45/15 |
55/40/5 |
55/40/- |
55/30/15 |
|
o |
60/50/30 |
60/50/20 |
60/50/20 |
60/45/10 |
60/45/5 |
60/35/20 |
|
n |
65/55/35 |
65/55/25 |
65/55/25 |
65/50/15 |
65/50/10 |
65/40/25 |
|
m |
70/60/40 |
70/60/30 |
70/60/30 |
70/55/20 |
70/55/15 |
70/45/30 |
|
l |
75/65/45 |
75/65/35 |
75/65/35 |
75/60/25 |
75/60/20 |
75/50/35 |
|
k |
80/70/50 |
80/70/40 |
80/70/40 |
80/65/30 |
80/65/25 |
80/55/40 |
|
j |
85/75/55 |
85/75/45 |
85/75/45 |
85/70/35 |
85/70/30 |
85/60/45 |
|
i |
90/80/60 |
90/80/50 |
90/80/50 |
90/75/40 |
90/75/35 |
90/65/50 |
|
h |
95/85/65 |
95/85/55 |
95/85/55 |
95/80/45 |
95/80/40 |
95/70/55 |
|
g |
100/90/70 |
100/90/60 |
100/90/60 |
100/85/50 |
100/85/45 |
100/75/60 |
|
f |
105/95/75 |
105/95/65 |
105/95/65 |
105/90/55 |
105/90/50 |
105/80/65 |
|
e |
110/100/80 |
110/100/70 |
110/100/70 |
110/95/60 |
110/95/55 |
110/85/70 |
|
d |
115/105/85 |
115/105/75 |
115/105/75 |
115/100/65 |
115/100/60 |
115/90/75 |
|
c |
120/110/90 |
120/110/80 |
120/110/80 |
125/110/75 |
120/105/65 |
120/95/80 |
|
b |
125/115/95 |
125/115/85 |
125/115/85 |
135/120/85 |
125/110/70 |
125/100/85 |
|
a |
130/120/100 |
130/120/90 |
130/120/90 |
145/130/95 |
135/120/80 |
130/105/90 |
|
aa |
- |
- |
- |
155/140/105 |
145/130/90 |
- |
|
ab |
- |
- |
- |
165/150/115 |
155/140/100 |
- |
|
ac |
- |
- |
- |
175/160/125 |
165/150/110 |
- |
|
ad |
- |
- |
- |
180/165/130 |
190/175/135 |
- |
|
ae |
- |
- |
- |
230/215/180 |
240/225/185 |
- |
|
af |
- |
- |
- |
280/265/230 |
290/275/235 |
- |
|
ag |
- |
- |
- |
330/315/280 |
340/325/285 |
- |
What is an Expansion Bolt?
An expansion bolt is a mechanical fastener used to fix objects to solid foundation materials such as concrete, bricks, and rocks. The following is a detailed introduction:
1. Structural composition
Expansion bolts are generally composed of screws, expansion tubes, washers, nuts, and other parts.
● Screws: Usually a fully threaded metal rod, one end of which is used to connect the object to be fixed, and the threaded part is used to tighten the nut to generate tension. The material of the screw is mostly carbon steel, alloy steel, etc. to ensure sufficient strength.
● Expansion tube: Generally, it is a tubular structure made of plastic (such as polyethylene) or metal (such as zinc alloy). Its outer diameter is slightly smaller than the diameter of the mounting hole. When the nut is tightened, the expansion tube will expand in the hole and tightly stick to the hole wall.
● Washers and nuts: Washers are placed between the nut and the fixed object to increase the contact area, disperse the pressure, and prevent damage to the surface of the fixed object; nuts are used for tightening, and tension is generated on the screw by rotating the nut to expand the expansion tube.
2. Working Principle
● First, drill a hole in the base material (such as the concrete wall in the elevator shaft). The diameter of the hole should be slightly larger than the outer diameter of the expansion tube. Generally, the appropriate hole diameter is determined according to the specifications of the expansion bolt.
● Insert the expansion bolt into the drilled hole to ensure that the expansion tube is completely inserted into the hole.
● When the nut is tightened, the screw will pull outward, causing the expansion tube to expand outward under radial pressure. Friction is generated between the expansion tube and the hole wall. As the nut is continuously tightened, the friction increases, and the expansion bolt is finally firmly fixed in the base material, so that it can withstand certain tensile force, shear force and other loads, so that the object (fixed bracket) connected to the other end of the screw is fixed.
Types of Expansion Bolts
1. Metal expansion bolts
Metal expansion bolts are usually made of zinc alloy or stainless steel, and their expansion tubes have high strength and strong load-bearing capacity. Suitable for occasions that need to withstand large tensile and shear forces, such as fixing heavy equipment, steel structure brackets, etc. Stainless steel material not only provides stronger corrosion resistance, but also can be used for a long time outdoors or in humid environments, ensuring the stability and durability of the installation.
2. Chemical expansion bolts
Chemical expansion bolts are fixed by chemical agents (such as epoxy resin). During installation, the agent is injected into the drilled hole, and after the bolt is inserted, the agent will quickly solidify, filling the gap between the bolt and the hole wall, forming a high-strength bond. This type of bolt is very suitable for occasions with strict requirements on fixing accuracy and vibration resistance, such as high-precision instruments and equipment or structural reinforcement applications.
3. Plastic expansion bolts
Plastic expansion bolts are made of plastic material, which is economical and easy to install. Suitable for fixing lighter objects, such as small pendants, wire troughs, etc. Although the load-bearing capacity is relatively low, its ease of operation and cost advantage make it an ideal choice for daily light installations.

Angle Brackets

Elevator Mounting Kit

Elevator Accessories Connection Plate
Packaging and Delivery

Wooden Box

Packing

Loading
How to correctly install expansion bolts?
1. Drilling precautions
● Position and angle:
When installing expansion bolts, use tools such as tape measures and levels to ensure accurate drilling positions. For building fixing solutions, such as equipment support or shelf installation, the drilling needs to be perpendicular to the installation surface to avoid loosening or failure of the expansion bolts due to uneven force.
● Depth and diameter:
The drilling depth should be 5-10mm deeper than the length of the expansion bolt, and the diameter should be slightly larger than the outer diameter of the expansion tube (usually 0.5-1mm larger) to ensure the expansion effect of the fastener.
● Clean the hole:
Remove dust and impurities from the drilled hole and keep the hole wall dry, especially when installing expansion bolts in humid environments to prevent affecting the performance of the metal expansion tube.
2. Choose expansion bolts
● Match specifications and materials:
Choose appropriate expansion bolts according to the weight, size and use environment of the object to be fixed. For outdoor or humid environments, stainless steel expansion bolts should be used to resist corrosion. In construction or industrial equipment installation, expansion bolts with larger diameters and higher strength are more suitable.
● Quality inspection:
Check the straightness of the screw of the fastener, the integrity of the thread, and whether the expansion tube is damaged. Expansion bolts with unqualified quality may lead to loose fixation and affect safety.
3. Installation and inspection
● Correct insertion and tightening:
Be gentle when inserting the expansion bolt to avoid damaging the expansion tube; use a socket wrench to tighten the nut to the specified torque to ensure the tightening effect.
● Inspection after fixing:
Verify whether the expansion bolt is firm, especially under high load conditions (such as large equipment installation), and check whether the fixed object is horizontal or vertical to meet the expected installation effect.
Multiple Transportation Options

Ocean Freight

Air Freight

Road Transportation












